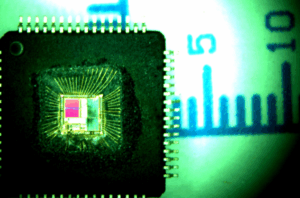
In today’s competitive and innovation-driven electronics industry, knowing how to prevent the microcontroller being copied is essential to protect intellectual property and maintain product integrity. With the rising sophistication of hardware reverse engineering, even secured microcontrollers (MCUs) are at risk of being cracked or cloned. Attackers deploy a variety of techniques to extract protected data from a chip and replicate it illegally.
The process typically starts with reverse engineering, where an adversary tries to decode or decrypt the firmware or binary stored in the microcontroller. By using methods like decapsulation—physically removing the chip’s outer layers—attackers can directly access the silicon die and probe the internal memory structures. Through this, they may attempt to dump, recover, or restore the encrypted program from the EEPROM or flash memory.
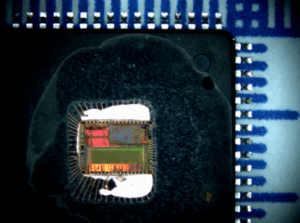
Copy Microcontroller Prevention has a great variety of methods, and burning out it read/write pinout circuit and its test terminal can effectively prevent the microcontroller copy. turn the pinout burning out from some general Microcontrollers could be an very effective way to increase the cost of copy Microcontroller. Similar method has also been applied on the smartcard, some of the terminals which have been used as the production test and flash programming, they can be wiped out physically after test.
Once the binary or hex file is extracted from the locked chip, it can be cloned or copied onto another microcontroller, allowing for unauthorized duplication of the original design. This kind of breach not only replicates the source code and critical data but also undermines the product’s security and commercial value.
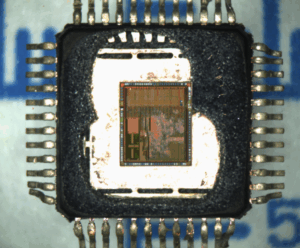
Common attack techniques include voltage glitching, fault injection, and side-channel attacks, which exploit vulnerabilities in the chip’s operation to break through security features. Even highly protected MCUs can sometimes be hacked using these advanced methods, giving attackers access to memory files and program archives.
Most of the Microcontroller is able to be read and written freely after the shielding of security fuse by the microcontroller copyer. Burn out one of the pinouts, even the security fuse has been wiped out, it can still prevent the external visiting from the programming on the memory. At the same time, most of the microcontrollers which base upon the flash memorizer can upgrade its program when copy microcontroller through the initiating block of user code area, without the usage of parallel programmer to avoid the microcontroller copy. write the initiation block before burn out, burn out won’t affect the upgrade of program.
To combat these threats, manufacturers must implement multiple layers of defense. Techniques such as secure bootloaders, encrypted firmware updates, and hardware-based security zones can drastically reduce the risk of binary file extraction. Disabling debug interfaces and using anti-tamper detection also make it harder for hackers to reverse engineer the chip.
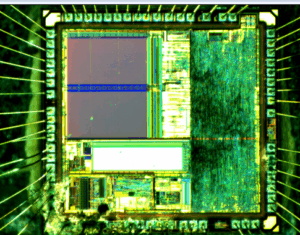
Understanding how attackers replicate, duplicate, or copy data from a secured microcontroller is the first step toward effective protection. Whether it’s a microprocessor in a medical device or an MCU in an industrial controller, ensuring the firmware and memory content remain confidential is vital. By staying informed and adopting a proactive security approach, companies can significantly reduce the risk of having their microcontroller copied or cloned.
It is very easy to burn out the pinout, add voltage, no matter the positive or negative, about reach the maximum value which the pinout lead can withstand, and it will has around 1A current to go through it which can cause the eternal damage on the transistor on the pinout lead: positive voltage on the high level can damage PMOS, negative voltage on the low level will damage NMOS to prevent the microcontroller copy.