In the realm of embedded systems and hardware security, the Extract MCU Protection Method is a term that encapsulates a set of techniques used to bypass the safeguards of a secured or locked microcontroller (MCU). As the demand for device firmware and embedded source code increases—often for legitimate purposes such as system recovery, reverse engineering, or legacy support—engineers and researchers have explored advanced methodologies to copy, clone, or recover data from protected chips.

MCUs often come with encrypted memory regions, including flash, EEPROM, or program archives, that are designed to prevent unauthorized access. However, with the right attack techniques, it’s possible to decrypt, dump, and even replicate the binary files stored within. This is where the Extract MCU Protection Method becomes crucial.
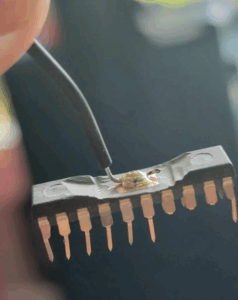
One of the most advanced strategies used in this field is decapsulation—a process that involves physically opening the microcontroller to access its internal circuitry. Through decapsulation, hackers or forensic engineers can examine the silicon die directly, sometimes using techniques like laser probing or electron microscopy to read memory contents bit by bit. This approach can effectively break the hardware-level encryption mechanisms, allowing the binary, firmware, or even source code to be recovered.
crack MCU embedded firmware need to know the part number, this is a most important information a MCU extracter should obtain in the first place. Without it, the MCU attacking process can’t be proceed immediately.
Print no marking on the MCU surface, print fake marking or re-print the new marking on the MCU surface can help to prevent microprocessor program cloning. In order to prevent the low level MCU breaking, and MCU manufacturers will usually wipe out the marking on the surface of MCU, but it can’t fend off the stuborn MCU attacker. Generally speaking, this method can effectively increase the MCU reverse engineering expenditure.

Through two methods can help to find MCU’s part number, one of them is monitor it under the microscopy after decapsulate the MCU outer package, since most of the MCU will have manufacturer name and MCU marking leave inside it. The other method will spend much less cost, microcontroller cracker can check their signal line, such as power supply, ground, clock or reset line. Since each one of MCU will have the unique pinout order of their own, which can help to ensure their general type.
In order to better prevent the MCU memory hacking and have better protection, MCU designer can wipe out the marking, or turn the MCU upside down, and treat the backside as top side. Or designer can cut off the leads on one side.
In less invasive methods, engineers may use firmware dumping tools or modified bootloaders to exploit firmware update mechanisms or communication protocols, effectively hacking into the MCU. With the right exploit, a device can be tricked into outputting its program data, allowing the user to replicate, duplicate, or clone the microcontroller’s contents.
Once a successful dump is made, the extracted binary can be disassembled and analyzed. Skilled analysts can recover the original source code logic, reconstruct the firmware, or even copy it to a new microprocessor—effectively cloning the functionality of the original device. This is particularly useful in cases of obsolescence or system failure where no original documentation is available.
While often associated with hacking, these methods are also vital in lawful cybersecurity research, digital forensics, and industrial data recovery. However, manufacturers are constantly evolving their chip protection designs, incorporating tamper-proof silicon, secure bootloaders, and advanced encryption to counteract these extraction techniques.
In conclusion, the Extract MCU Protection Method is a sophisticated field that blends electronics, cryptography, and reverse engineering. Whether used to crack a locked firmware, decrypt an encrypted archive, or recover a vital file from a damaged chip, these techniques are at the cutting edge of embedded system security and analysis.
If designer need to better protect the MCU, MCU can use un-standard footprint and package, such as COB (Chip On Board), they can even print the marking on the MCU by themselves. But this method is only suitable for the mass production of electronic product, some MCU manufacturers can provide this kind of service, some MCU manufacturers can also pre-programme the MCU and print the customized marking on them.
