Chip extract binary technology is a specialized field that focuses on retrieving binary files from secured or protected chips such as microcontrollers (MCUs) and microprocessors. This technique is used to dump or copy the internal firmware, flash, EEPROM, or program memory from a locked or encrypted chip. Often used in reverse engineering, system recovery, or legacy device replication, this process requires advanced technical knowledge and precision tools.
The core of chip extract binary technology lies in its ability to extract and decode the binary or source code stored in an embedded chip. These chips are usually designed with built-in security features to prevent unauthorized access. However, through a series of advanced methods—such as decapsulation, microprobing, fault injection, or side-channel attacks—engineers can break the protection mechanisms and recover the hidden data.
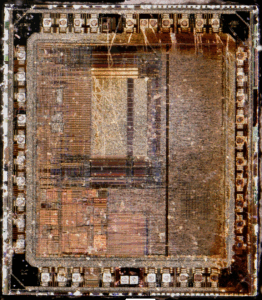
Decapsulation involves physically opening the chip’s package to access the silicon die. Once the chip is exposed, precise instruments can be used to locate and interact with the memory areas where firmware or flash data is stored. In more advanced cases, hackers may use scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) to analyze the electrical activity in the MCU and capture the program output.
Chip Extract binary Technology can be diversified as three different ways, they are un-invasive, semi-invasive and invasive Extract Microcontroller Firmware methods. And also there is a very deep blank area within the gap between un-invasive and invasive extract, and there are a lot of technologies belongs to this chip extract heximal method, is much cheaper than the invasive chip extract, and its repeatibility is similar to un-invasive attack.
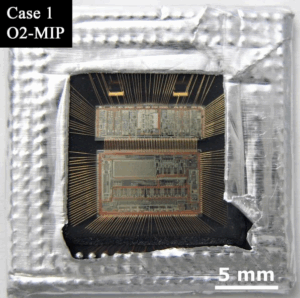
Semi-Invasive Copy Microcontroller Program method need to decapsulate the chip to visit and access the chip die just like invasive chip extract method does. But it can keep the deactivation layer impact and unspoiled. Semi-invasive chip extract doesn’t need to strip off the deactivation layer or create the internal connection without using the expensive equipment such as microprobe, focus ion beam, laser cutting, etc.
Semi-invasive Microcontroller Unlocking eeprom is not the whole new set of technology, decades ago in the microcontroller chip which use EEPROM or OTP rom, designer will use ultra-violet to shield the security fuse. Modern microcontroller chip seldom being recovered by this kind of technology so had been taken into consideration ever since.
Advanced Imaging Technology can also be the semi-invasive chip firmware extract skill. Include the infrared radiation, laser scanning and thermal imaging. Some of them can be used on the rear side of chip, it is very impactful on the modern chip which has the multilayer metal design. Some of these technologies can even observe the individual transistor inside chip.
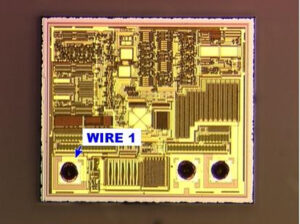
Another approach involves software-based hacks that exploit weaknesses in the bootloader or debug interface to clone, replicate, or duplicate the embedded file system. When successful, the archive of internal data can be exported as a full binary dump—a complete digital image of the original chip‘s content.
In some cases, the data may be encrypted, requiring further steps to decrypt and decode the binary. Once decrypted, the firmware can be analyzed, modified, or used to build a functional copy of the original system. This capability is invaluable for legacy system maintenance, security audits, and competitive analysis.
While chip extract binary technology has legitimate applications in system recovery and industrial cloning, it also raises ethical and legal questions when used to crack or hack proprietary systems. As technology evolves, chip makers continue to enhance protection features, making the art of extraction a constantly evolving battle between defense and offense in the embedded world.
