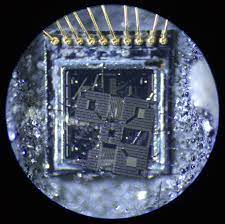
Extracting microcontroller firmware is a highly technical process often required in reverse engineering, embedded system analysis, or legacy system restoration. When a microcontroller (MCU) or microprocessor is secured, protected, or encrypted, accessing its internal flash memory or EEPROM becomes a complex task. Engineers, researchers, and hackers may attempt to extract microcontroller firmware to recover critical data, analyze source code, or replicate the behavior of legacy systems no longer supported by manufacturers.
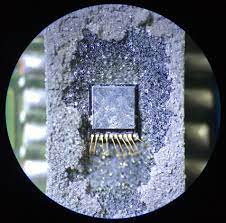
Modern chips implement advanced security mechanisms such as code locking, encrypted firmware storage, and readout protection. These protections aim to prevent unauthorized attempts to copy, clone, or duplicate the firmware or program stored within the device. However, certain scenarios—such as forensic recovery, competitive analysis, or system migration—may justify the need to dump or decode a locked firmware file.
Several techniques exist to break or crack these protections. For example, invasive attacks such as chip decapsulation involve physically removing the protective layers of the MCU to access its internal circuitry and memory. Once exposed, specialized equipment can read or recover binary data directly from the silicon. This raw data may require further steps to decrypt or decode, especially if the firmware was encrypted or compressed.

Extract Microcontroller Firmware will need to use laser lighting or even the cheap flash light, both these tools are all necessary for the fault injection Microcontroller Unlocking method. Sometimes due to the limitation on the budget, as well as the un-stable performance of laser light, sometimes the microcontroller extracter can use the low cost flash lamp. Although flash lamp’s luminosity is lower than pulse laser, but after proper modification amplification can also reach the ionic level which is required for microcontroller copying. Fix the flash lamp onto the video terminal and amplifier 1500 times.
After the microcontroller has been programmed, the firmware embedded can be uploaded or downloaded. Fill the memorizer of microcontroller with constant voltage and expose in the flash lamp when microcontroller extracting, read out the result and then can understand the modification of unit status after inspection on the process of Extract Chip Code.
Through the hole on the aluminum sheet can shield the light source, the output power of light source can be set to the maximum when Extract MCU AT89C5130A Code. We can also change a unit’s status. The final status of unit depends on the exposed area in the flash lamp which can almost assure microcontroller extracter that semi-invasive extract will change the content in the SRAM.