Extracting microcontroller code is a critical technique in the field of embedded system analysis and hardware reverse engineering. It involves the process of retrieving binary files from a secured chip, such as a locked or encrypted microcontroller (MCU) or microprocessor. Often, this technology is used to recover or replicate valuable firmware, source code, or EEPROM contents when the original design data is lost, damaged, or intentionally protected.
Modern chips often come with secured, encrypted, or locked configurations to prevent unauthorized access. However, with specialized tools and techniques, experts can decapsulate the chip, dump its memory, and decode the internal program stored in flash or archive formats. This process may involve attacking the chip at the hardware or software level using techniques like fault injection, power analysis, or physical probing.
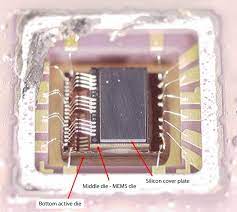
Extract Microcontroller Code include a series of different methods and all of these methods can be separated into three kinds, first is the invasive microcontroller unlocking, second is semi-invasive microcontroller code extraction, third is non-invasive microcontroller code extraction.
Software stimulation extraction method is one of the most effective ways for non-invasive chip code extraction analysis method. We can add Laser impulse to P type transistor grid where is 10 microns area, microcontroller attacker can assume that the turning around will occur when the output voltage is higher than the input voltage with 1 logic value, It is much higher than normal reversor threshold value voltage, but with the absence of internal precise threshold value voltage information from microcontroller internally.

As we checked before, the stimulation result is same, and with great area on the microcontroller will response to the laser’s energy. It can turn the reversor around completely without the locked effect when extract mcu at89ls51 firmware. This kind of difference could be bigger in the shorter wavelength laser. It is because the silicon will absorb the short wavelength laser energy and cause the increasing quantity of ion pairs beneath the transistor grid. From one side, it will improve the modification ability in the channel, from other side, it decrease the current from N type transistor and make the parasite structure become more difficult to turn around.
Professionals may crack, break, or hack the security layers of a microcontroller to copy, clone, or duplicate its contents for legitimate purposes such as system recovery, interoperability, or failure analysis. By bypassing security, the extracted binary or data file can then be decrypted and converted back into readable source code or firmware.
Although often viewed as controversial, the ability to extract microcontroller code is crucial for legacy system support, IP validation, and industrial security assessments. It enables engineers to recover critical data from damaged or obsolete systems and ensures the continuity of technological operations.
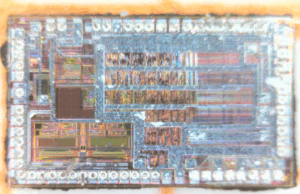
As embedded systems continue to evolve, so do the methods to extract, analyze, and replicate the protected contents of a microcontroller. Understanding and applying these techniques responsibly is key to maintaining system integrity in today’s highly digitized environment.
